Overview
The Smart-Contract Version Control and Rollback Governance system creates an established and trackable system which handles all stages of smart contract management including their improvement and retirement and emergency restoration procedures. The system restricts all modifications to on-chain logic to be performed through clear and verified governance systems which restrict independent or hidden changes to contracts. The system changes smart contracts into operational systems which organizations can control through established governing processes.
Purpose and rationale
Smart contracts become permanent after their initial deployment according to common belief but require updates which developers use to correct errors and enhance their efficiency and handle new regulatory requirements and operational needs. The absence of structured version control introduces significant risk.
The most serious protocol failures occurred because of silent upgrades and rushed patches and privileged admin keys. The system reduces that risk through its requirement of strict change management which operates directly on the blockchain.
Scope of application
The system applies to all production smart contracts that control assets, permissions, execution logic, or governance processes. The system provides support for core protocol contracts and upgradeable modules and parameter contracts and emergency control components. The framework exists as a chain-agnostic system which public and private and consortium blockchain environments can use.
Versioning and provenance
Every contract version is assigned a unique identifier and cryptographic hash that represents its exact bytecode and configuration. The version metadata displays three deployment attributes which include deployment timestamp and activation status and superseded versions and governance approval reference. The system creates an unchangeable record which documents all changes made to the contract after the information gets recorded.
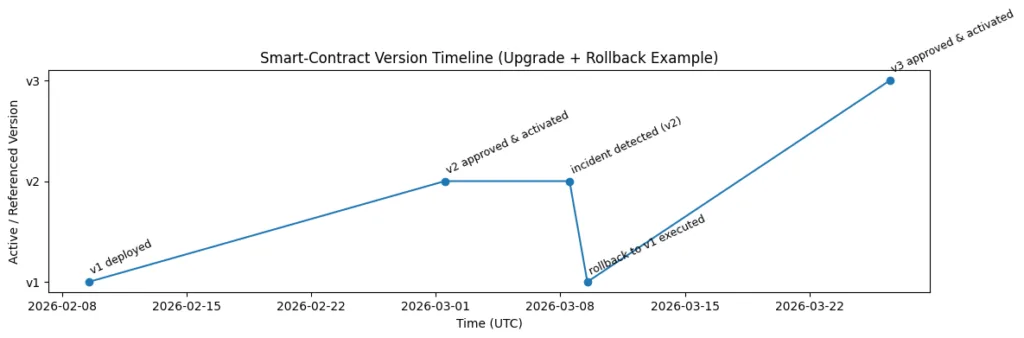
Upgrade governance process
The process of upgrades follows a structured governance system that consists of multiple stages. The proposed changes are submitted through upgrade candidates which link to their targeted contract and specific software version.
The governance participants need to examine the proposal together with its associated risks and all implementation details before they can approve it. The organization executes the approved upgrade according to its established rules which enable both predictable outcomes and protection against unanticipated modifications.
Rollback and emergency control
The system provides controlled rollback capabilities which enable users to restore the system to its earlier approved contract version during critical failures and system exploits and cases of unknown system behavior.
The system requires specific permission to execute rollbacks because these actions function as mandatory events which create permanent records that stay on the blockchain. The system creates emergency response mechanisms which enable organizations to handle emergencies while maintaining oversight and tracking of their response activities.
Transparency and auditability
The system keeps an on-chain record of every operation which includes all proposals and all approvals and all executions and all rollbacks and all deprecations. The system establishes a complete record which documents who approved changes together with the specific times of those changes and the software versions that were active during that period. Auditors and regulators can reconstruct contract state with cryptographic certainty rather than relying on off-chain documentation.
Access control and separation of duties
The framework requires distinct separation between three phases of design work which include proposal submission and approval authority and execution activities. The contract logic of the system cannot be altered by any single person. Smart contracts define and enforce specific roles and permissions which help to minimize risks from insider threats and key security breaches.
Compliance and risk management value
From a regulatory and institutional perspective, Smart-Contract Version Control & Rollback Governance demonstrates operational maturity. It shows how contract modifications are handled with due diligence while emergency authority usage is restricted and system activities can be traced back to their previous state. The particular usability of this system becomes critical when dealing with financial operations and asset custody management and compliance monitoring activities.
Strategic value
The smart contract system becomes operational through this feature because it enables organizations to use smart contracts in their business operations. The system decreases protocol risks while building stakeholder trust and supporting continuous system development which maintains both transparency and system reliability. The system establishes a secure governance framework through its combination of audit trails and on-chain policy registries.