Market context
The decentralized finance ecosystem has reached its current state after coming from its original liquidity mining period. Total value locked has become a reliable measurement that now shows actual market conditions instead of previous measurement errors. Investors now commit their funds to built-up systems which use staking derivatives and restaking primitives and tokenized real-world assets and perpetual futures collateral pools and automated lending markets. The system shows its highest level of complexity yet.
The system requires people to work at the same time because it needs multiple parts to work together across different parts. DeFi users now use multiple assets as collateral because they need to secure their positions. The system provides financial institutions with multiple layers of protection which they can use to select their most effective risk management methods. Staked ETH becomes liquid staking tokens. Staked ETH transforms into liquid staking tokens. Restaking tokens function as collateral used for staking and restaking. Restaked derivatives become inputs for liquidity pools. Users can use liquidity pool tokens as their margin.
The system uses borrowed stablecoins for perpetual trading operations.The same unit of base capital often supports multiple claims simultaneously.The financial system shows hidden dangers because people can use reused assets yet maintain their market stability.
may be entering a similar structural phase. The question is not whether growth is occurring. The question is whether the quality of collateral backing the system is deteriorating as complexity increases.The narrative describes an imminent collapse. The study investigates the structural foundation.
The collateral stack explained
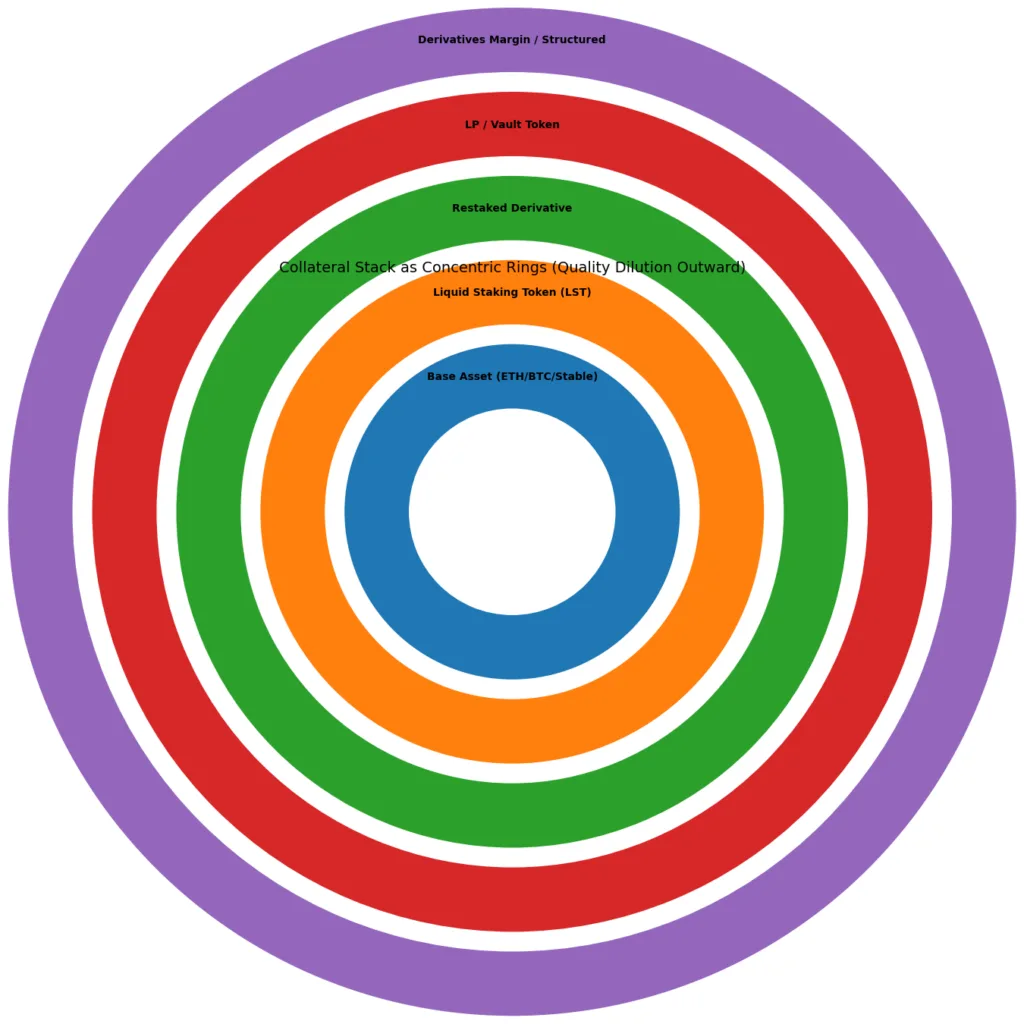
The fundamental characteristics of high-quality collateral require it to maintain liquidity and unencumbered status while showing complete asset disclosure. In the beginning of decentralized finance, users employed their native digital currencies and stablecoins as collateral assets. The assets displayed obvious risk patterns which made them easier to understand. The contemporary technology framework exceeds current systems because of its increased complexity.
Base asset layer
The system depends on three primary assets which include native ETH and native BTC and the main stablecoins. The value of these assets originates from their connection to network security and their usage by customers and their ability to provide liquid market conditions.
Derivative collateral layer
Liquid staking tokens like stETH function as ownership rights to the staked ETH which they represent. The system introduces three types of risk which include smart contract risk and validator performance risk and liquidity basis risk.
Restaking layer
Restaked derivatives enable users to maintain their current staking activities while obtaining extra benefits. The system achieves better capital efficiency but results in multiple services sharing the same risk exposure.
Synthetic and structured layer
Liquidity pool tokens, yield-bearing vault tokens, and structured strategy tokens embed leverage together with asset-specific risk which their respective strategies introduce. The financial instrument exhibits multiple risk components which include market risk together with smart contract risk and liquidity risk.
The operational behavior of capital in the stack system needs to follow a specific route because its risk assessment becomes more complex through subsequent stages. The process of transformation creates new variables which depend on existing conditions. The collateral may still appear valuable on paper, but its liquidity and loss characteristics change materially.The deeper the stack, the more assumptions underpin stability.
Rehypothecation chains and hidden leverage
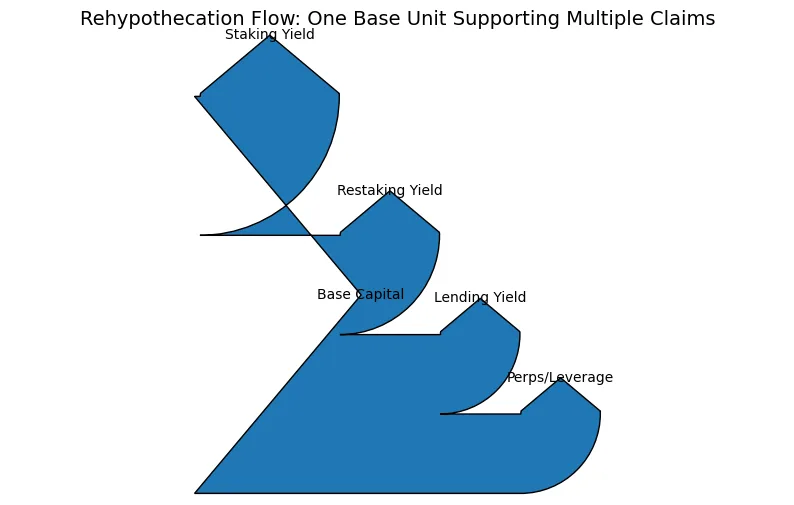
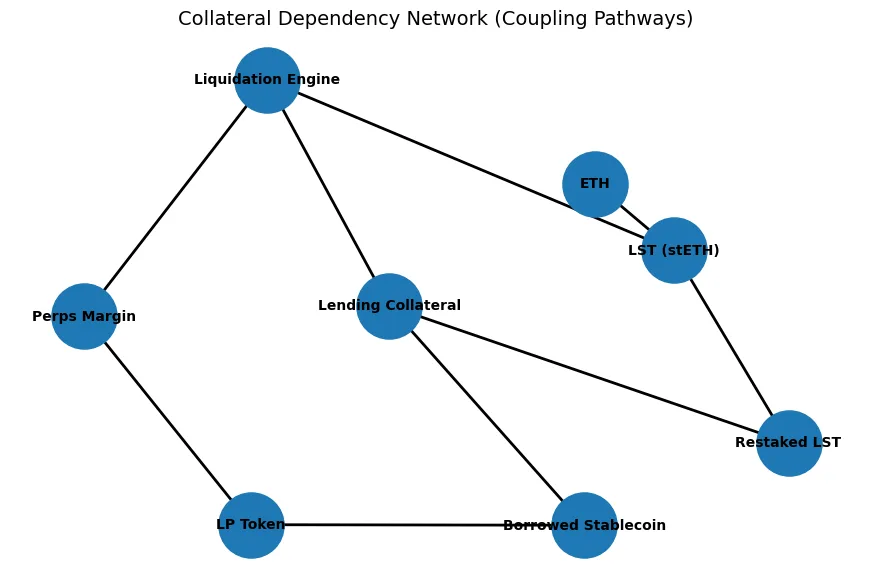
Rehypothecation in traditional finance refers to the reuse of pledged collateral to support additional borrowing. DeFi uses automated processes for transparent operations although these activities produce identical results to traditional finance systems.Consider a simplified chain.An investor stakes ETH and receives a liquid staking token. The token restaking process transfers the token into a shared security framework. The restaked token serves as collateral for a lending protocol deposit. The stablecoins which are borrowed from the liquidity pool become active in the liquidity pool which generates LP tokens.
The LP tokens function as margin for trading on the perpetual futures platform. The original ETH generates multiple benefits which include staking rewards restaking rewards lending yield and liquidity pool incentives and leveraged derivatives exposure. The same economic base supports multiple claims which are created at each stage. The layered structure creates operational efficiency which becomes evident during normal market conditions. During periods of extreme stress all linked systems experience simultaneous price declines. Liquidations cascade because every protocol contains design flaws yet all systems share the same fundamental risk. The system develops tight coupling between its components.
Stress scenario modeling
The research The study investigates fragility through a simulated stress condition.ETH will lose 30 percent of its value during the upcoming brief period according to this scenario. Liquid staking tokens currently trade at a temporary discount because of their restricted liquidity. Restaked services encounter two issues which include validator instability and the possibility of slashing risk occurring in related systems.
The lending platforms experience a decrease in collateral value which results in assets reaching their liquidation points. Borrowers who need to sell their assets to repay loans create stablecoin liquidity problems. Multiple protocols initiate their liquidation processes because many positions use the same collateral types. The process of deleveraging gets speeded up through the use of automated systems. The primary factor that determines the system status is the depth of available liquidity.
If derivative collateral trades at a discount to underlying ETH during stress, collateral ratios calculated on nominal value may overestimate true exit value. Liquidation systems fail to stop bad debt creation when these conditions exist. The system operates with two forms of fragility which include price volatility and system-wide commodity price safekeeping. The system experiences collateral impairment across various levels which results in increased asset correlation. The system demonstrates tranche stacking in structured finance because it lacks visible capital protection mechanisms.
The Real-world asset dimension
The stack receives an extra component through the implementation of tokenized real-world assets. People use tokenized treasuries and private credit instruments as partnerships that provide secure backing because they generate reliable income and maintain high security levels. RWAs create three problems which include settlement delays and off-chain legal enforcement challenges and difficulties with asset redemption. RWA-backed tokens do not achieve liquidation at the same pace as on-chain systems during times of liquidity emergencies.
DeFi lending markets create a collateral mismatch because they use RWAs as collateral while on-chain margining operates at different speeds than off-chain asset verification. Yield becomes attractive during stable market conditions. Stressful situations make redemption periods essential because they take precedence over yield. The system creates two different types of asymmetry which affect duration and liquidity in collateral systems.
Measuring collateral quality
To assess narrative performance through collateral quality assessment, four assessment dimensions must be used. The first dimension assesses liquidity depth which exists during stressful situations. The second dimension measures encumbrance level which indicates the quantity of extra claims that exist on the same base asset. The third dimension evaluates correlation exposure which exists between different protocols.
The fourth dimension compares redemption speed to liquidation speed. The system achieves resilience through its unencumbered collateral assets which maintain high liquidity and exhibit low correlation between different layers. The system requires the same asset to undergo multiple transformations for use in different protocols but its design creates structural vulnerabilities. The relationship between capital efficiency and resilience established a pattern of reverse connection.
Systemic risk comparison
The comparison to traditional structured finance is instructive but should not be exaggerated. DeFi operates through fundamental systems which differ from traditional frameworks. The system operates its liquidation engines through automated processes which maintain complete visibility.
The system displays its existing collateral ratios to all users. The system has no hidden over-the-counter balance sheet elements that would conceal their actual exposures. The system uses transparent data yet the system still has correlation risk. The same derivative collateral form which appears in multiple lending markets will cause liquidation cascades to operate in synchronized fashion.
The year 2008 saw the emergence of fragility because organizations used hidden leverage while the housing market experienced simultaneous price changes. In decentralized finance systems the base-layer crypto volatility which affects collateral transformation will create fragile conditions. The system does not require fraud to experience stress. The system needs only synchronized repricing to function.
Toward a risk-weighted collateral framework
The next evolution of DeFi may require more sophisticated collateral weighting models. protocols should create dynamic haircut systems that use two factors to assess the value of their derivative collateral instead of valuing derivative collateral at near-par to its base asset. Restaked derivatives would need to maintain higher margin requirements during market volatility spikes. RWA-backed tokens could include redemption speed buffers in liquidation calculations.Such models would reduce capital efficiency in exchange for structural stability.As institutional participation increases, risk-aware collateral modeling will likely differentiate mature protocols from opportunistic yield platforms.